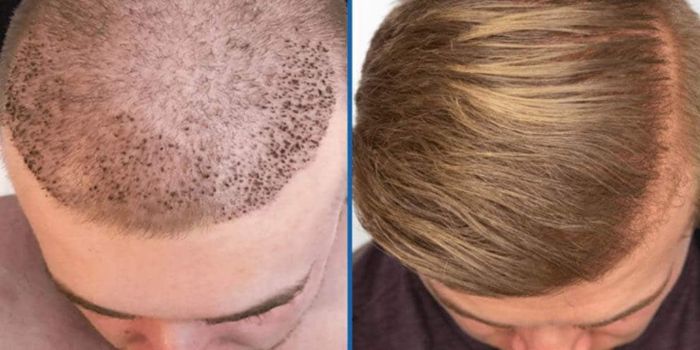
Patients frequently ask me, as a hair transplant surgeon with more than 7 years of experience doing both FUE and FUT operations, to assist them in selecting the best technique for their unique requirements and expectations. Both FUE and FUT have benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to know the main distinctions between these two widely used hair restoration methods. Let’s read below about “FUE vs. FUT: Which Hair Transplant Method is Right for You?”.
Table of Contents
My Personal History Performing
FUT and FUE I worked as a senior hair transplant surgeon’s assistant and observer for the first three years of my profession after earning my MBBS and focusing in plastic and cosmetic surgery. I worked on hundreds of surgeries using the FUE and FUT techniques during this long training period.
I only did FUT surgeries when I first opened my own clinic because most patients were more accustomed to strip harvesting at that time. But now that I’m more proficient at FUE extraction and have observed the excellent patient satisfaction rates, I do three times as many FUE surgeries as FUT.
I have completed about 900 hair transplant surgeries in my career, more than 600 of which included FUE. I’ve been able to use both strategies to get fantastic outcomes because to this experience.
FUE Hair Transplant Method
Using a specialized punch tool, individual follicular units are taken directly from the donor area in a less invasive hair transplant procedure known as follicular unit extraction, or FUE.
According to my observations, a number of significant advantages make FUE a desirable choice for a large number of my patients:
Minimally Invasive – Strip harvesting leaves only microscopic spots in the donor region, preventing the formation of a lengthy, linear scar. It takes a lot less time to recuperate than with FUT.
Fewer Restrictions on Hair Length – While strip harvesting is most effective with longer hair in the donor location, the punch instrument can extract grafts from hair of any length.
Potential for Body Hair Transplants – FUE enables patients who lack enough scalp donor hair to use body hair from parts like the arms, chest, and beard as donor grafts.
However, there are some downsides to FUE that patients should be aware of:
Higher Graft Transaction Rate – Compared to strip harvesting, hand extraction has a greater risk of follicular damage, rendering some extracted grafts unsuitable for transplantation. This may result in fewer grafts being obtained overall.
Longer Procedure Time – FUE procedures typically last longer than FUT since physically extracting each individual graft requires a significant amount of time and skill.
Increased Cost – Compared to FUT, FUE is a more costly operation overall because to the need for specialist instruments, longer OR time, and staff support.
FUT Hair Transplant Method
The process of follicular unit transplantation involves taking a strip of tissue from the donor region and utilizing stereo microscopes to separate it into individual follicular units.
FUT offers the following advantages to the right candidate:
Maximizes Graft Yield – More total hairs can be extracted than with FUE extraction when a strip of tissue is carefully removed and trimmed into grafts by skilled professionals.
Quicker Sessions – More grafts can be retrieved each hour when the strip harvesting procedure is combined with contemporaneous graft dissection.
Cost-Effective – Although there are trade-offs with a linear donor scar and a lengthier recovery period, FUT is less expensive per graft than FUE.
However, there are also some distinct disadvantages that patients should consider with strip harvesting:
Visible Linear Scar – For a lot of patients, the thought of having a lengthy scar line restricts their options for hairstyles.
Nerve Damage Risk – There is a little possibility that removing the donor strip would harm sensory nerves, which could result in numbness.
Extended Recovery – Compared to the small FUE extraction sites, larger strip removal wounds require more time to heal completely. Avoiding strenuous activities is required for a minimum of three weeks.
Making the Right Choice Between FUE and FUT
After carefully assessing your unique circumstances, you should decide between a FUE or FUT hair transplant based on your own tastes. In my clinic, I talk to patients about the following important deciding elements during consultations:
- Available Donor Hairs and Desired Coverage – Due to higher graft yields, patients who need more than 3,000 grafts to get their desired level of coverage typically see superior results from FUT.
- Donor Hair and Scalp Laxity – Whether FUE or FUT is preferable depends on how flexible and loose the skin is in the donor area. Tight scalps frequently facilitate strip excision for FUT, but laxity enhances the effectiveness of FUE graft extraction.
- Recovery Expectations – In order to minimize downtime, people with hectic schedules or those who are hesitant to restrict activities for longer than a few days typically choose FUE. FUT requires more thorough wound healing for two to three weeks following surgery.
- Willingness to Cut Hair – A buzzcut or extremely short hairdo is comfortable for certain people, which is ideal for a FUT treatment. But FUE allows surgery with lengthier locks for people who don’t want to cut their hair very short.
- Cost Considerations – Although the sessions need more time, FUT usually results in a 20–30% reduction in graft costs. Strip harvesting therefore becomes a preferable option for those who are severely budget conscious.
- Follow-Up Treatments – To get the best coverage, you may need more than one session. Starting with FUE lets you save the option to harvest FUT strips later.
- Camouflaging Donor Scars – People who tan easily, have dark scalps, or wear their hair very short are less likely to notice noticeable FUE dot scarring and are more likely to be able to disguise the linear FUT scar.
Conclusion
In certain instances, a hybrid strategy that combines FUE and FUT in separate sessions can reduce obvious donor scarring while maximizing graft yield for greater coverage. Hybrid strategy can use the advantages of each distinct harvesting technique.
Success in every elective operation depends on education and matching expectations to reality. Depending on the patient’s stage of hair loss and the features of the donor hair, hair transplantation still has restrictions even if amazing results are undoubtedly possible.
I usually tell patients straight up if getting a hair transplant is really the best course of action or whether there are more acceptable options available to them given their existing circumstances, such as medication or concealers.
If you want to have surgery to restore your hair, you should talk to a board-certified dermatologist or plastic surgeon who specializes in hair transplantation. They can advise you on whether you’re a good candidate and, if so, which technique—FUE, FUT, or combination approach—will best help you achieve your desired cosmetic results. I hope you like reading “FUE vs. FUT: Which Hair Transplant Method is Right for You?”.

Kannaiah Thallapally is a seasoned hair restoration expert with a strong background in advanced hair transplant techniques. As an Associate Member of the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgeons (ISHRS), Kannaiah combines his extensive knowledge with a commitment to the latest industry practices. His expertise is showcased on hairstransplant.in, where he provides valuable insights into hair restoration solutions. Kannaiah is dedicated to helping individuals achieve their desired results and restore their confidence. Connect with him on Instagram for more updates and expert tips.